C#中Foreach循环遍历的本质与枚举器详解
对于C#里面的Foreach学过 语言的人都知道怎么用,但是其原理相信很多人和我一样都没有去深究。刚回顾泛型讲到枚举器让我联想到了Foreach的实现,所以进行一番探究,有什么不对或者错误的地方大家多多斧正。
1、创建一个控制台应用程序
2、编写测试代码并分析
在Program类中写一个foreach循环
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List peopleList = new List() { "张三", "李四", "王五" };
foreach (string people in peopleList)
{
Console.WriteLine(people);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
生成项目将项目编译后在debug目录下用Reflection反编译ForeachTest.exe程序集后查看Program类的IL代码,IL代码如下:
.class private auto ansi beforefieldinit Program
extends [mscorlib]System.Object
{
.method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname instance void .ctor() cil managed
{
.maxstack 8
L_0000: ldarg.0
L_0001: call instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor()
L_0006: ret
}
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 2
.locals init (
[0] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string> list,
[1] string str,
[2] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string> list2,
[3] valuetype [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1/Enumerator`0<string> enumerator,
[4] bool flag)
L_0000: nop
L_0001: newobj instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string>::.ctor()
L_0006: stloc.2
L_0007: ldloc.2
L_0008: ldstr "\u5f20\u4e09"
L_000d: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string>::Add(!0)
L_0012: nop
L_0013: ldloc.2
L_0014: ldstr "\u674e\u56db"
L_0019: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string>::Add(!0)
L_001e: nop
L_001f: ldloc.2
L_0020: ldstr "\u738b\u4e94"
L_0025: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string>::Add(!0)
L_002a: nop
L_002b: ldloc.2
L_002c: stloc.0
L_002d: nop
L_002e: ldloc.0
L_002f: callvirt instance valuetype [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1/Enumerator`0<!0> [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<string>::GetEnumerator()
L_0034: stloc.3
L_0035: br.s L_0048
L_0037: ldloca.s enumerator
L_0039: call instance !0 [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1/Enumerator`0<string>::get_Current()
L_003e: stloc.1
L_003f: nop
L_0040: ldloc.1
L_0041: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
L_0046: nop
L_0047: nop
L_0048: ldloca.s enumerator
L_004a: call instance bool [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1/Enumerator`0<string>::MoveNext()
L_004f: stloc.s flag
L_0051: ldloc.s flag
L_0053: brtrue.s L_0037
L_0055: leave.s L_0066
L_0057: ldloca.s enumerator
L_0059: constrained. [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1/Enumerator`0<string>
L_005f: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.IDisposable::Dispose()
L_0064: nop
L_0065: endfinally
L_0066: nop
L_0067: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.ConsoleKeyInfo [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadKey()
L_006c: pop
L_006d: ret
.try L_0035 to L_0057 finally handler L_0057 to L_0066
}
}
在反编译的IL代码中我们看到除了构建List和其他输出,然后多了三个方法:GetEnumerator(),get_Current() ,MoveNext() ,于是通过反编译reflector查看List泛型类,在List里面找到GetEnumerator方法是继承自接口IEnumerable 的方法,List实现的GetEnumerator方法代码
public Enumerator GetEnumerator() => new Enumerator((List) this);
即返回一个Enumerator泛型类,然后传入的参数是List泛型自己 this。接下来查看 Enumerator<T>泛型类
[Serializable, StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator
{
private List<T> list;
private int index;
private int version;
private T current;
internal Enumerator(List<T> list)
{
this.list = list;
this.index = 0;
this.version = list._version;
this.current = default(T);
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
List<T> list = this.list;
if ((this.version == list._version) && (this.index < list._size))
{
this.current = list._items[this.index];
this.index++;
return true;
}
return this.MoveNextRare();
}
private bool MoveNextRare()
{
if (this.version != this.list._version)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EnumFailedVersion);
}
this.index = this.list._size + 1;
this.current = default(T);
return false;
}
public T Current =>
this.current;
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get
{
if ((this.index == 0) || (this.index == (this.list._size + 1)))
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EnumOpCantHappen);
}
return this.Current;
}
}
void IEnumerator.Reset()
{
if (this.version != this.list._version)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EnumFailedVersion);
}
this.index = 0;
this.current = default(T);
}
}
我们看到这个Enumerator<T>泛型类实现了接口IEnumerator的方法,也就是我们测试的ForeachTest程序集反编译后IL代码中出现的get_Current() ,MoveNext() 方法。所以foreach实际上是编译器编译后先调用GetEnumerator方法返回Enumerator的实例,这个实例即是一个枚举器实例。通过MoveNext方法移动下标来查找下一个list元素,get_Current方法获取当前查找到的元素,Reset方法是重置list。
3、总结
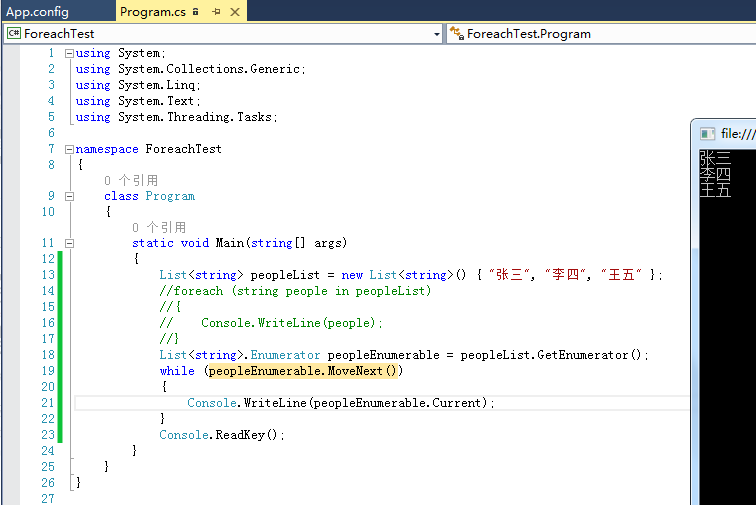
因此要使用Foreach遍历的对象是继承了IEnumerable接口然后实现GetEnumerator方法。返回的实体对象需要继承IEnumerator接口并实现相应的方法遍历对象。因此Foreach的另一种写法如下。
关于C#中Foreach循环遍历本质与枚举器的文章就介绍至此,更多相关C# Foreach循环与枚举器内容请搜索编程教程以前的文章,希望大家多多支持编程教程!
迭代器模式平时用的不多,因为不管C#还是Java都已经帮我封装了,但是你是否知道平时经常在用的东西本质是怎么回事呢。看完迭代器模式你就知道C# foreach循环是怎么实现的了,我的另一篇C# Foreach循环本 ...
